Human sleep patterns appear to change with seasons |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › seasonal changes › Human sleep patterns appear to change with seasons |
Human sleep patterns appear to change with seasons
| Changes in the seasons affect myriad forms of life on Earth. Deciduous trees shed their leaves in fall before regrowing them in spring. Bears, squirrels, turtles, and various other animals hibernate, their metabolisms falling to a near standstill. The snow hare and ermine don brown fur in summer and white fur in winter. And as a new study finds, humans seem to be seasonal as well, experiencing marked changes in the duration and structure of our sleep throughout the year. Winter is sleep seasonScientists primarily based out of the Clinic for Sleep & Chronomedicine at St. Hedwig Hospital in Berlin conducted the research. It was published recently in the journal Frontiers in Neuroscience. The team invited 188 volunteers (98 women and 90 men) to each spend three nights in a laboratory setting where their rest could be closely monitored. The participants came in for the analysis at various times throughout the year. In the lab, the volunteers were encouraged to snooze during their preferred time and to sleep in. As they slept, their brain waves, blood oxygen level, heart rate, breathing, eye movements, and leg twitches were all recorded, a process collectively called polysomnography. Humans sleep in two distinct phases, rapid eye movement (REM) and non-rapid eye movement (NREM), the latter of which is further divided into three stages. Polysomnography allows scientists to classify a sleeper’s shut-eye into these categories. As the monthly data revealed, subjects tended to sleep longer during the winter, by up to 60 minutes (though the result barely missed statistical significance); they took about 25 minutes shorter to enter into REM sleep during autumn than spring; they experienced about 30 minutes more REM sleep on average in winter than spring; and they underwent a swift and sudden drop in slow-wave sleep (the deepest form of NREM sleep, during which we dream and our memories consolidate) in the fall months. 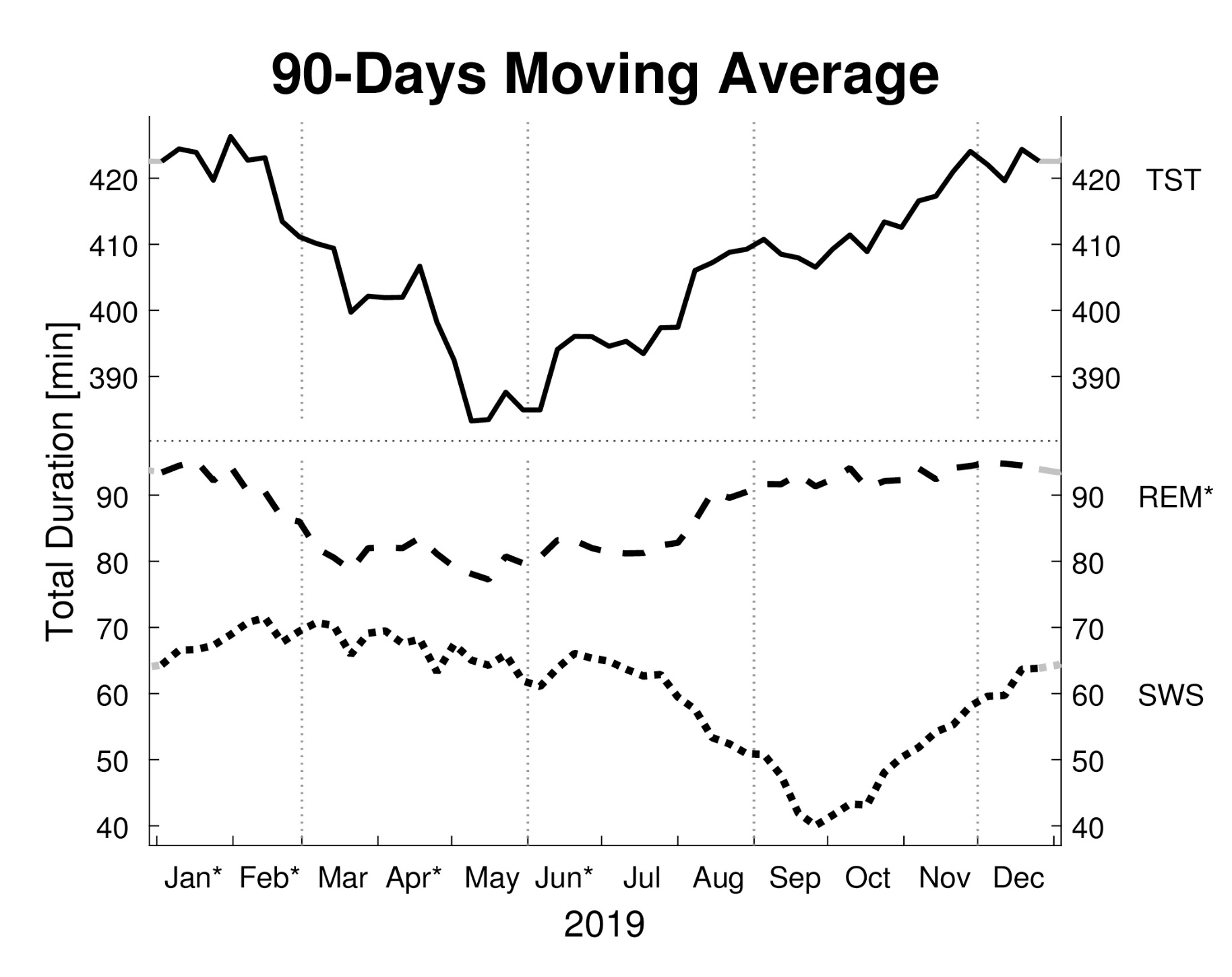 Moving averages for selected sleep parameters. (Credit: A. Seidler et al., Front Neurosci, 2023) Moving averages for selected sleep parameters. (Credit: A. Seidler et al., Front Neurosci, 2023)The findings fall in line with a previous study conducted by the authors in which thousands of subjects subjectively reported sleeping longer in the winter. But still, the current results do defy conventional wisdom. By mastering artificial light, humans were thought to have mostly rid themselves of the tyranny of sunlight, which — through biological mechanisms — heavily affects the behavior of most living things on the planet. Even though all the subjects were urban dwellers in a large, modern metropolis where light is pervasive, their sleep still showed seasonality. However, it must be noted that the study group was relatively small, the subjects all had a condition which prompted difficulty sleeping (primarily insomnia or depression), and, again, the difference in sleep duration between summer and winter was statistically non-significant (though likely to be real given other evidence). “This study needs to be replicated in a large cohort of healthy subjects,” Kunz cautioned. Can’t override the SunStill, there’s a simple takeaway, a salubrious recommendation that anyone can adopt. “Our findings suggest that improvements can be made by accounting for the increased sleep need in winter, by going to bed earlier,” the authors wrote. In a statement, Dr. Dieter Kunz, corresponding author of the study, noted that though humans have mostly made themselves masters of the planet, they do not yet appear to have overcome their ingrained seasonality. “Seasonality is ubiquitous in any living being on this planet. Even though we still perform unchanged, over the winter human physiology is down-regulated, with a sensation of ‘running-on-empty’ in February or March. In general, societies need to adjust sleep habits including length and timing to season, or adjust school and working schedules to seasonal sleep needs.” |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
点击排行 |
|
推荐新闻 |
图片新闻 |
|
专题文章 |